The United Arab Emirates ranks among the top countries with a high Human Development Index. It is characterized by a high level of safety and the absence of most taxes, which positively impacts the quality of life for both native residents and migrants. The government creates an extremely favorable environment for attracting investments, making the UAE a popular destination for both budding entrepreneurs and established businesspeople from other countries.
This article will provide detailed information on the economic and religious features of the UAE, along with guidance on how to obtain residency. It will also cover what is required for relocation and offer insights into where and how to live in the UAE from a geographical perspective. Furthermore, we’ll talk about profitable commercial activities, procedures for opening company, cost of living in different cities, and addresses other important questions that arise when considering immigration to another country.
Country Specifics

The UAE is a multinational federated state in the Middle East with a developed economy, where anyone can realize their potential. The country is located on the coast of the Persian Gulf, with much of its territory covered by desert.
Life in the emirates is governed by Muslim traditions and laws, but citizens and the legislative base of the country are always loyal to representatives of other religions and cultures. Statistics show that 9 out of 10 residents of the UAE are foreigners.
Economy and standards of living in UAE
The UAE is often associated with oil and gas. However, it is incorrect to say that the UAE’s economy relies solely on the extraction and sale of petroleum products. Today, the revenue from oil and gas activities makes up only about 30% of the country’s GDP.
According to the International Monetary Fund, the UAE ranks 7th in the world for GDP per capita, surpassing developed countries like the United States and Germany.
The country has relatively low inflation rates, with an average annual rate of just 0.2%.
The creation of Free Economic Zones (FEZs) has spurred innovation in the economy, attracting top specialists from various business fields worldwide.
Language and religion
The only official language in the UAE is Arabic. However, English is also widely used and is seen and heard everywhere. Signage and other public information often have English translations. It is also common practice to legalize documents in English. English is widely used for international communication in government structures, with tourists, in business centers, etc. Even government service mobile apps are adapted for English-speaking users.
The state religion is Islam, and most migrants also practice this faith (about 90% of the population). Over the years, strict religious rules have been relaxed to attract labor migrants for work in the UAE. A notable example is the lifting of restrictions on the purchase, consumption, and storage of alcohol in 2020.
Is it expensive to live in the UAE?
At first glance, the cost of living in the UAE might seem high due to the high rental prices. The high demand for rental properties is driven by a large influx of people from abroad, as migration to the UAE is currently popular among residents of central Europe.
The average monthly salary is 19,500 AED, varying greatly depending on the job position, qualifications, city, and other factors. There is no concept of a minimum subsistence level in the UAE. Overall, the income level here ensures a high purchasing power for the average family.
Real estate

Compared to excellent earning opportunities, real estate prices in the UAE are considered low, even with the increase in 2022. For example, a 90-square-meter apartment in Dubai costs about $200,000, with annual maintenance costs around $8,000.
Most often, real estate is purchased in the Dubai Marina and Business Bay areas, with the most expensive and elite residences located on Palm Jumeirah and in Downtown Dubai.
Statistically, homes are purchased five times less frequently than apartments.
The real estate market is favorable for investors from around the world. This is due to the low property prices relative to rental costs. Despite the high monthly rental rates (about $9,000 on average in Dubai), demand remains high among tourists and businesspeople who come to the UAE for business events.
The annual return on investment in real estate after taxes reaches 8%, making it a promising vector for investment.
Taxes
The UAE tax system is known for its leniency towards individuals and businesses, with minimal tax rates and the absence of certain taxes that are commonly paid in most other countries around the world. Residents do not pay income tax, pension contributions, luxury taxes, dividends, and capital gains, as well as taxes on exports.
Types of taxes in the United Arab Emirates:
- local taxes: set by the government of one of the seven emirates;
- federal taxes: set at the national level;
- taxes within FEZs: operate with different preferential regimes for foreign individuals who own companies within the free economic zone;
- other taxes and fees: include non-business-related charges.
Summary table of personal taxes in Dubai
| Tax name | Amount or percentage | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Tourist tax | 6-10% | Paid upon visiting local attractions |
| Municipality tax | 7% | Calculated based on the cost of a hotel room, food, drinks, and service |
| Tourism Dirham | 7-20 AED/day | Charged for hotel stays, but only for the first 30 days of residence/td> |
| Vehicle registration fee | 420 AED | Annual vehicle registration renewal required |
| Vehicle ownership transfer fee | 350 AED | One-time payment |
| Business license fees | – | Amount depends on the type of activity chosen |
| Property transfer fee | 4% | Based on property value |
| Property registration fee | 2000 (for properties up to 500,000 AED) and 4000 (for properties over 500,000 AED) | Paid by the buyer |
| Property transfer charge | 540 AED | Added to the transfer fee |
| Value Added Tax (VAT) | 5% | Paid upon purchasing commercial real estate |
Summary table of corporate taxes in Dubai
| Tax name | Amount or percentage | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| VAT | 5% | Paid by companies with annual revenue exceeding 375,000 AED |
| Corporate tax (profit tax) | 9-55% (depends on the industry) | Applies to firms with annual revenue over 375,000 AED. Some FEZs offer exemptions |
| Excise tax | 50-100% | Percentage varies by product category |
| Import tax | 5-100% | Zero rate applies for businesses in free zones |
Healthcare and education
Healthcare in the UAE is of high quality, with patient safety being a top priority. Residents with a visa receive medical services for free, but every citizen must have insurance, costing from $500 per year. Employers provide insurance for their employees, while others must purchase it themselves.
Note that lacking an insurance policy can result in fines.
The UAE’s education system is standardized according to British, American, and European requirements. Nurseries, schools, and higher education institutions offer free services only to UAE citizens. If you are not a citizen, be prepared to pay a significant amount for these services.
Living in the UAE: pros and cons of relocation

If you are considering how to immigrate to Dubai or any other UAE city, we advise to weigh the pros and cons.
Key advantages of moving to the UAE:
- no need to speak Arabic to feel comfortable here – many areas of activity and daily life require only English proficiency;
- no personal income tax;
- tax and other incentives for businesses;
- no corruption;
- residents can open bank accounts;
- ease of starting a new company;
- many privileges for promising startups;
- a decent standard and living conditions in Dubai and other emirates;
- small businesses do not pay corporate tax;
- good working conditions and decent salaries for employees;
- warm climate (which can also be a disadvantage if you have heat-related health issues);
- ability to move with the whole family;
- access to quality education;
- advanced healthcare system;
- road infrastructure is recognized as the best in the world.
However, immigration to the UAE also has its flip side. The disadvantages include:
- high rental costs;
- prices for many goods are higher than in European countries;
- public transportation is poorly developed on some territories, requiring regular car rentals;
- need for thorough understanding of local laws and customs to avoid issues related to religion and traditions.
Immigration methods
To obtain a residence visa in the UAE, you need to contact the nearest embassy and provide the required documents. If residency is being granted for education or employment with a UAE-based company, an invitation from the educational institution or employer is mandatory.
For individuals who have obtained residency status but have been absent from the UAE for more than six months without a valid reason, the residence visa may be canceled. For those residing continuously in the UAE, residency can be renewed indefinitely. A long-term residence visa can be issued for 5-10 years after three years of legal residency in the country. Citizenship can be acquired no sooner than thirty years of legal residency in the UAE.
Let’s explore each legal way to stay in the UAE in more detail, including some helpful tips for living in Dubai and other emirates.
Investments
Investing in the UAE economy or purchasing property is one way to immigrate to Dubai for permanent residence.
The table below outlines scenarios for obtaining a residence visa through investment.
| Type of investment | Minimum investment amount (AED) | Type of residence | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Property purchase | 750 000 | Visa | 24 months |
| Property purchase | 2 000 000 | Golden Residence Visa | 10 years |
| Business activity | 100 000 | Visa | 2 years |
A key requirement is that the resident must prove a stable monthly income for the next 36 months from the date of property transfer or business license issuance.
Employees in top positions with a salary of at least 30,000 AED per month are also eligible for a 10-year Golden Visa (a diploma is required).
For more information on what business is in demand in Dubai and the types of investment companies in the UAE, click here.
Business Immigration
Entrepreneurs can start a business in the UAE through two legal routes. The first option is becoming a business partner in an existing UAE company or establishing a new company. The residency period depends on meeting specific conditions and the type of activity. Examples are shown in the table below.
| Investment amount (AED) | Visa duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| No capital requirements | 1-2 years | Suitable for startups that have passed a “casting” in one of the UAE business incubators |
| From 100000 | Up to 10 years | Investments in industry, services, or other business types regulated by the issued license |
Long-term residency allows the holder to request residence visas for three company executives, as well as their relatives and other family members.
The 10-year Golden Visa allows the applicant to request residency for their business partners.
Employment immigration

If you think “How can I move to Dubai”, or you are ready to move to the UAE, are a skilled professional, fluent in English, and have a job offer from an employer, employment migration might be the right path for you. UAE law requires local employers to cover the immigration costs for expatriates (visa fees, initial accommodation, medical examination, etc.), making it financially comfortable for foreign workers.
A residence visa is usually issued for a maximum of two years, except for top-tier specialists who receive a 10-year Golden Visa.
The salary amount is fixed by the terms of the employment contract and cannot be lower than what is specified in the contract.
Education
Entry permits for students are issued only if the following requirements are met:
- an official request from an accredited university;
- minimum acceptable scores on the secondary education certificate;
- proficiency in English;
- payment of the first year of tuition in the UAE (typically $5,000-10,000).
The student visa is valid for 12 months and can be renewed for each subsequent year of study. During the study period, employment is strictly prohibited. Upon graduation, international students can obtain residency as labor migrants or a Golden Visa if they have excellent grades and high academic performance in college or university.
How to move to UAE?
Entering the UAE as a tourist does not require a visa. For stays up to 30 days (which can be extended to 90 days through immigration authorities), you only need a valid passport and medical insurance.
If your purpose of entry is business, education, employment, or any other reason for a longer stay, you will need a residence visa.
How to obtain permanent residency?
The main steps in the process of obtaining permanent residency are:
- Collecting documentation (required documents include proof of property ownership, an employment contract, medical certificate, bank statement, passport, and photos). Some documents may need notarization.
- Applying for a short-term or long-term visa to enter the country.
- Moving to the UAE.
- Applying for a Residence Visa – this can be done online (through the federal portal eChannels) or offline (at Amer centers).
- Issuing an Emirates ID.
- Applying for permanent residence after three years of legal residence in the UAE. Early application for permanent residency is possible if you have a signed contract with an employer for 36 months.
- Obtaining citizenship requires fluency in Arabic and at least 30 years of residence in the UAE. Exceptions are women who marry a UAE citizen; they can obtain citizenship 15 years after marriage.
How to choose an emirate?
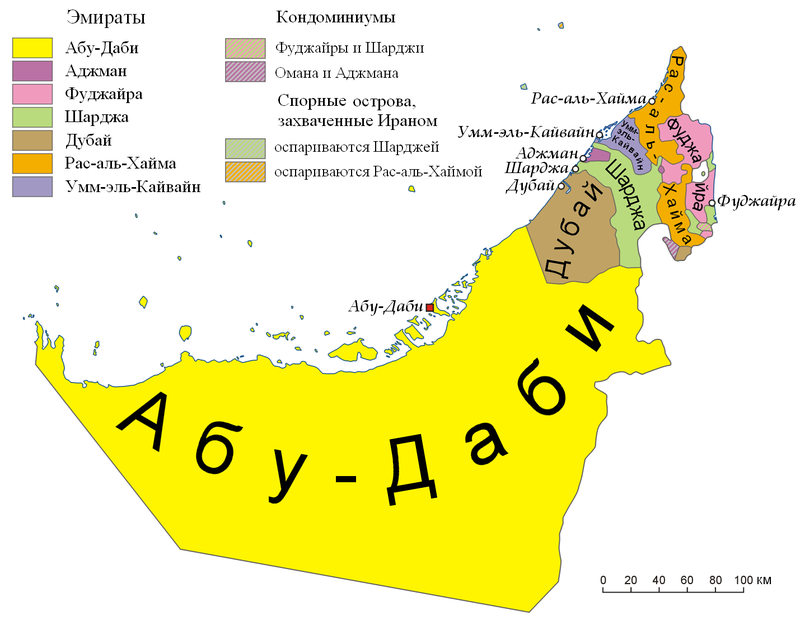
The UAE is divided into seven emirates, each essentially functioning as separate monarchies. These are:
- Abu Dhabi — The largest and wealthiest emirate, occupying 87% of the total area, and is the capital of the UAE;
- Dubai — The second-largest emirate, covering 5% of the area;
- Ras Al Khaimah;
- Fujairah;
- Umm Al Quwain;
- Sharjah;
- Ajman.
Dubai or Abu Dhabi: where is it better to live?
To relocate to Dubai and live there, you first need legal residence in the UAE and a stable income above the average, as the cost of services, food, and real estate in Dubai is higher than in other emirates. However, the high standard of living, advanced technology sector, and stunning architecture in Dubai make the financial cost worth it.
Abu Dhabi offers equally great opportunities. For example, in the capital, there are government programs for gifted students, privileges for top-tier professionals, and attractive investment opportunities for those working in Abu Dhabi.
Where to settle? It all depends on your goals and personal preferences.
Free Zones in the UAE
If you think: “How can I move to Dubai?” and your main goal is to start a new company and conduct business, don’t focus only on Abu Dhabi and Dubai. Other emirates have excellent logistics solutions, such as proximity to international airports and seaports, and offer unique benefits for setting up businesses in Free Zones. Detailed information on specific Free Economic Zones in each emirate can be found here.
Conclusion
The UAE is a country with a growing economy and minimal tax burden. It is ideal for ambitious foreigners looking for high-paying jobs, where in 5-10 years you can accumulate a starting capital for creating your own business; for receiving quality education with a future prospect of staying and well-paying in one of the emirates; for investment activities; or starting and growing a business.
Qualified specialists at Dynasty Business Adviser can assist with document legalization and, if necessary, help you set up a company from start and professionally guide you through all registration stages.









